nForum
Not signed in
Want to take part in these discussions? Sign in if you have an account, or apply for one below
Site Tag Cloud
Vanilla 1.1.10 is a product of Lussumo. More Information: Documentation, Community Support.
If you want to take part in these discussions either sign in now (if you have an account), apply for one now (if you don't).
-
- CommentRowNumber1.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeJan 24th 2010
- (edited Jan 25th 2010)
In the past we had some discussion here about why simplicial methods find so much more attention than cubical methods in higher category theory. The reply (as far as I am concerned at least) has been: because the homotopy theory = weak oo-groupoid theory happens to be well developed for simplicial sets and not so well developed for cubical sets. Historically this apparently goes back to the disappointment that the standard cubical geometric realization to Top does not behave as nicely as the one on simplicial sets does.
Still, it should be useful to have as much cubical homotopy theory around as possible. Many structures are more naturally cubical than simplicial.
So as soon as the Lab comes up again (we are working on it...) I want to create a page model structure on cubical sets and record for instance this reference here:
Jardine, Cubical homotopy theory: a beginning
-
- CommentRowNumber2.
- CommentAuthorTobyBartels
- CommentTimeJan 25th 2010
The Lab is back, so here is a bump with a better spelt link: model structure on cubical sets.
-
- CommentRowNumber3.
- CommentAuthorzskoda
- CommentTimeJan 25th 2010
So, why not following Grothendieck, considering any test category ?
-
- CommentRowNumber4.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeJan 25th 2010
here is a stub: model structure on cubical sets
(and the spelling in the above comment has now magically improved, too :-)
-
- CommentRowNumber5.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeJan 25th 2010
- (edited Jan 25th 2010)
So, why not following Grothendieck, considering any test category ?
Do we have model category structures, generally, for these?
By the way, in that entry when you say "classifying space"
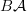 of a category
of a category 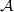 you mean (the realization of) its nerve, right?
you mean (the realization of) its nerve, right?I am sot sure we should call that classifying space, even though I know that it is often called that. Can we just call it the nerve, or the Kan fibrant replacement of the nerve, or the realization of the nerve?
Or else we should do something. For instance the entry on classifying space should spend some words on pointing out that there is some terminological flexibility. Currently it effectively starts with saying that a classifying space is a representing object.
-
- CommentRowNumber6.
- CommentAuthorzskoda
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
- (edited Jan 26th 2010)
We should still call it the classifying space of a category, because, as your boss points out, the classifying space of a category C classifies the C-torsors. This is true even if C is not a group(oid), provided the correct definition of a torsor is taken.
http://mathoverflow.net/questions/11045/are-non-empty-finite-sets-a-grothendieck-test-category
I am not educated in the homotopy theory of Grothendieck, but I suppose that the answer to your question is not. You have weak equivalences and you have a homotopy theory, but I think of a bit more general kind that the one which is treatable by Quillen's axiomatics. In the weak equivalence business being Quillenisable is a tricky question.
Maltsiniotis: pdf
Oh no, I am wrong. It seems Jardine says yes, see his survey, theorem 6.2 for the more complicated case involving A-presheaves on a site. The homotopy theories of A-sets for all test categories A are equivalent if I understand the story.
-
- CommentRowNumber7.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
- (edited Jan 26th 2010)
We should still call it the classifying space of a category, because, as your boss points out,
I heard that. May I still disagree? Don't tell him! ;-)
the classifying space of a category C classifies the C-torsors.
Yeah, but every space X classifies something, namely
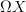 -torsors. My impression is that the Moerdijk category-torsors are torsors over the oo-groupoid fibrantly replacing the category, that's why these spans appear. They form the groupoidification of the category. And this means that the result really has nothing intrinsically to do with the original category. As we discussed with Mike recently, in the context of the notion of "cohomology of a category".
-torsors. My impression is that the Moerdijk category-torsors are torsors over the oo-groupoid fibrantly replacing the category, that's why these spans appear. They form the groupoidification of the category. And this means that the result really has nothing intrinsically to do with the original category. As we discussed with Mike recently, in the context of the notion of "cohomology of a category".But in any case, even if we were interested for other reasons in such torsors, it's not these torsors that play a role in the discusison of test categories. I think it only is good style to call something a classifying object if one was previously talking about the things it classifies. Otherwise I could call every object whatsoever a classifying object. When you ask me what it classifies, I just say it classifies the homotopy fibers of morphisms into it. That's always true. But can be besides the point.
Anyway, I won't fight over this terminological issue. But I will want to add at least some clarifying remarks to the entry classifying space, sometime later.
-
- CommentRowNumber8.
- CommentAuthorzskoda
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
- (edited Jan 26th 2010)
Algebraic geometers often do say that every space is a moduli space of its own (functor of) points. But surely, as you point out, there are natural moduli problems where a functor to describe is rather important or simple. It is the matter of an area of research which ones are good enough to locally deserve the name. More logically minded person can even think weather a functor to represent is definable in this or that sense, to deserve calling its representing object of some possibly generalized, kind a moduli space (or stack or pro-object etc.).
I do not get which torsors "play a role in the discussion if test categories" ? What are you alluding to ?
-
- CommentRowNumber9.
- CommentAuthorHarry Gindi
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
- (edited Jan 26th 2010)
The paper by Jardine cited on the page about test categories is really quite interesting. Question, if any of you know: Is there any evidence for a similar result, but about the Joyal model structure? That is, that paper shows that for any test category A, A-Sets has a model structure that's quillen equivalent to the Kan model structure. Has there been work on "porting" the Joyal model structure from SSets to A-Sets?
-
- CommentRowNumber10.
- CommentAuthorzskoda
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
The work of Cisinski on the subject is so massive that it is hard to believe that the extension is not attempted.
-
- CommentRowNumber11.
- CommentAuthorzskoda
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
- (edited Jan 26th 2010)
I have placed a link (into test category) to joyalscatlab:Cisinski's book... where a short overview placing test categories into context is written by Joyal (actually copied from Cisinski's abstract I guess).
-
- CommentRowNumber12.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeJan 26th 2010
Thanks Zoran.
Very interesting to see what Andre Joyal is doing on his web. I am glad we made this web come into existence-
-
- CommentRowNumber13.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeNov 30th 2010
added some details to model structure on cubical sets
-
- CommentRowNumber14.
- CommentAuthorTim_Porter
- CommentTimeNov 30th 2010
- (edited Nov 30th 2010)
@Zoran your link to Joyal’s pages is to the ncatlab.org version so give the picture of the girl! It is easy enough to change for anyone who gets this, but you may want to adjust the source to make things neater. (Yours is not the only link that is not working as Joyal’s link to Cisinski’s pdf file is dead. It needs a d in front of the name.)
-
- CommentRowNumber15.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeNov 30th 2010
- (edited Nov 30th 2010)
Tim,
you realize that Zoran’s message is from almost a year ago? I don’t think we want to go and manually change each and evry link already.
-
- CommentRowNumber16.
- CommentAuthorUrs
- CommentTimeDec 1st 2010
added to model structure on cubical sets the reference to with comments on Gugenheims “supercomplexes” that Peter May mentioned on the AlgTop-list. But I have not found and seen the article myself yet.
-
- CommentRowNumber17.
- CommentAuthorspitters
- CommentTimeOct 22nd 2014
Re #16: The paper is available online now. I’ve added a link.
-
- CommentRowNumber18.
- CommentAuthorTim Campion
- CommentTimeFeb 2nd 2019
-
- CommentRowNumber19.
- CommentAuthorRichard Williamson
- CommentTimeFeb 2nd 2019
-
- CommentRowNumber20.
- CommentAuthorMike Shulman
- CommentTimeFeb 3rd 2021
Added a link to cubical-type model structure and its non-equivalence to spaces.
-
- CommentRowNumber21.
- CommentAuthorDmitri Pavlov
- CommentTimeNov 28th 2021
-
- CommentRowNumber22.
- CommentAuthorDmitri Pavlov
- CommentTimeNov 28th 2021
I am removing the following remark, which I find misleading. In his paper, Gugenheim introduces what nowadays could be termed “multisimplicial sets”, i.e., presheaves of sets on the full subcategory of simplicial sets comprising finite products of simplices (of any dimension). Of course, one can extract a cubical set from such a multisimplicial set, but they are not the same notion.
There is also the old work
- Victor Gugenheim, On supercomplexes Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 85 (1957), 35–51 PDF
in which “supercomplexes” are discussed, that combine simplicial sets and cubical sets (def 5). There are functors from simplicial sets to supercomplexes (after Defn 5) and, implicitly, from supercomplexes to cubical sets (in Appendix II). This was written in 1956, long before people were thinking as formally as nowadays and long before Quillen model theory, but a comparison of the homotopy categories might be in there.
-
- CommentRowNumber23.
- CommentAuthorDmitri Pavlov
- CommentTimeNov 28th 2021
Added:
Cubical sets with connections
The following paper proves that cubical sets with connection form a strict test category and therefore admit a cartesian model structure that is Quillen equivalent to the Kan–Quillen model structure on simplicial sets:
- Georges Maltsiniotis, La catégorie cubique avec connexions est une catégorie test stricte, Homology, Homotopy and Applications 11:2 (2009), 309-326. doi.
-
- CommentRowNumber24.
- CommentAuthorDmitri Pavlov
- CommentTimeNov 28th 2021
Added:
Cubical sets with max-connections and min-connections
The case of cubical sets with both max-connections and min-connections largely follows the case of cubical sets with max-connections, the corresponding category of cubes again being a strict test category. The relevant results are stated explicitly as Corollary 3 and Theorem 3 of
- Ulrik Buchholtz, Edward Morehouse, Varieties of Cubical Sets, arXiv.
-
- CommentRowNumber25.
- CommentAuthorDavid_Corfield
- CommentTimeMay 2nd 2023
-
- CommentRowNumber26.
- CommentAuthorEvan Cavallo
- CommentTimeDec 29th 2024
1 to 26 of 26